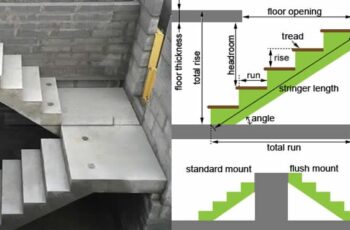
Structural engineering is a vital discipline within civil engineering that focuses on designing and analyzing structures that support or resist loads. These structures include buildings, bridges, dams, towers, and many other infrastructure components that form the backbone of modern society. Understanding what structural engineering entails and why it matters is essential for appreciating how our built environment is safely and efficiently created.
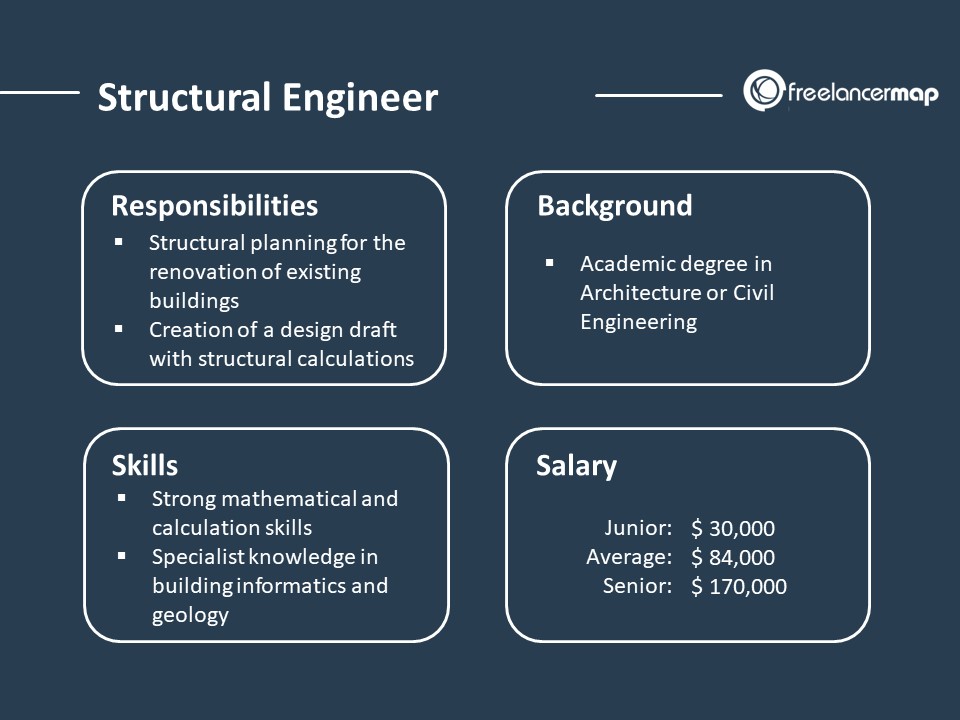
Introduction to Structural Engineering
At its core, structural engineering involves ensuring that structures can withstand the forces and loads they encounter during their lifespan. This includes everything from the weight of the structure itself to environmental forces like wind, earthquakes, and snow, as well as human-induced loads such as traffic or occupancy.
Structural engineers apply principles of physics and mathematics to calculate the strength, stability, and rigidity of structures. They select appropriate materials (such as steel, concrete, timber, or composites) and design structural systems that are safe, economical, and durable.
The History of Structural Engineering
The practice of structural engineering dates back thousands of years. Ancient civilizations, from the Egyptians to the Romans, built remarkable structures like pyramids, aqueducts, and temples without modern technology but with keen understanding of materials and forces.
The Industrial Revolution marked a turning point, introducing new materials like steel and reinforced concrete, and enabling the construction of taller, longer, and more complex structures. Modern structural engineering continues to evolve with advances in computer modeling, materials science, and construction techniques.
Key Responsibilities of Structural Engineers
Structural engineers are involved in a wide range of activities throughout a project’s lifecycle:
- Design: Creating structural plans and specifications that outline how a building or infrastructure will be constructed to meet safety and performance requirements.
- Analysis: Using computational tools and hand calculations to assess how a structure will respond to different loads and conditions.
- Material Selection: Choosing materials that provide the necessary strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Inspection and Testing: Assessing existing structures for safety and recommending repairs or reinforcements.
- Collaboration: Working closely with architects, contractors, and other engineers to ensure a cohesive and efficient design.
Types of Structures Designed by Structural Engineers
Structural engineers design a variety of structures, each with unique challenges and considerations:
- Buildings: Residential, commercial, industrial, and skyscrapers.
- Bridges: Suspension, beam, arch, and cable-stayed bridges that span waterways and valleys.
- Towers and Masts: Communication towers, transmission line towers, and observation towers.
- Dams and Reservoirs: Structures that control water flow and generate hydroelectric power.
- Offshore Structures: Platforms and rigs for oil and gas extraction in marine environments.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Airports, tunnels, and railway stations.
Why Structural Engineering Matters
Safety and Public Welfare
The primary goal of structural engineering is to safeguard lives and property. Structural failures can lead to catastrophic losses, injuries, and fatalities. Proper design and construction ensure that buildings and infrastructure can withstand everyday use and extreme events like earthquakes and storms.
Economic Impact
Well-designed structures are cost-effective over their lifespan. Structural engineers optimize material use and construction methods to reduce costs while maintaining safety. Avoiding structural failures also saves enormous amounts in repair, litigation, and human costs.
Enabling Innovation and Growth
Structural engineering enables the creation of innovative architectural designs and large-scale infrastructure projects. Skyscrapers, long-span bridges, and sustainable buildings all depend on advanced structural engineering to become feasible.
Environmental Sustainability
Structural engineers contribute to sustainability by designing durable structures that minimize resource use and waste. They also help integrate renewable energy systems and support green building certifications.
The Structural Engineering Design Process
The design process typically follows several stages:
- Preliminary Design: Understanding project requirements, site conditions, and initial conceptual layouts.
- Analysis: Calculating loads, stresses, and deflections using software and engineering principles.
- Detailed Design: Developing detailed drawings, specifications, and selecting materials and structural systems.
- Review and Approval: Ensuring compliance with codes and standards and obtaining necessary permits.
- Construction Support: Assisting contractors during construction to address issues and ensure design intent is met.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Monitoring structures post-construction to ensure long-term performance.
Challenges Faced by Structural Engineers
Structural engineers face numerous challenges, including:
- Complex Loads and Conditions: Designing for dynamic loads like earthquakes and wind requires sophisticated analysis.
- Material Limitations: Balancing strength, durability, and cost within material constraints.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating building codes, safety standards, and environmental regulations.
- Sustainability Goals: Incorporating eco-friendly practices without compromising safety or cost.
- Technological Changes: Keeping up with new materials, construction techniques, and software tools.
The Role of Technology in Structural Engineering
Modern structural engineering relies heavily on technology:
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Enables precise and efficient drafting of structural plans.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA): Allows detailed simulation of structural behavior under various loads.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): Facilitates collaboration and integration across disciplines.
- Advanced Materials: Use of composites, high-strength concrete, and smart materials improves performance.
- Automation and Robotics: Enhances construction accuracy and safety.
Education and Skills Required
To become a structural engineer, typically a degree in civil or structural engineering is required, along with professional licensure. Key skills include:
- Strong foundation in mathematics and physics.
- Proficiency in structural analysis and design software.
- Understanding of materials science.
- Problem-solving and critical thinking.
- Communication and teamwork abilities.
Case Studies: Structural Engineering in Action
The Burj Khalifa, Dubai
The tallest building in the world, the Burj Khalifa, showcases advanced structural engineering. Its unique “buttressed core” design provides exceptional stability against wind and seismic forces while enabling an unprecedented height of 828 meters.
The Millau Viaduct, France
This cable-stayed bridge is the tallest in the world and demonstrates the use of high-strength materials and aerodynamic design to span the Tarn River valley with minimal environmental impact.
Earthquake-Resistant Buildings in Japan
Japan’s structural engineers have pioneered seismic design techniques, such as base isolation and energy dissipation systems, to protect buildings in one of the most earthquake-prone regions on Earth.
Future Trends in Structural Engineering
- Sustainable Structures: Greater emphasis on carbon-neutral and energy-efficient designs.
- Smart Structures: Integration of sensors and IoT for real-time monitoring and maintenance.
- Modular and Prefabricated Construction: Accelerating building timelines and reducing waste.
- Artificial Intelligence: Enhancing design optimization and predictive maintenance.
- Resilient Infrastructure: Designing to withstand climate change impacts and natural disasters.
Conclusion
Structural engineering is fundamental to the safety, functionality, and sustainability of the built environment. It combines scientific principles, creativity, and practical knowledge to design structures that support our daily lives and future growth. As society faces new challenges like urbanization and climate change, the role of structural engineers becomes even more critical in creating resilient and innovative infrastructure.
Understanding what structural engineering is and why it matters helps us appreciate the complexity and importance of the structures that surround us and the professionals who design them. Whether it’s the skyscraper where you work, the bridge you drive over, or the home where you live, structural engineering plays a key role in ensuring these structures are safe, reliable, and enduring.