Construction sites are inherently dangerous places, with numerous risks that can lead to serious injuries or fatalities if not properly managed. Ensuring safety on these sites is paramount to protect workers and maintain productivity. This comprehensive blog post explores the 10 most common construction safety hazards, providing insights into each hazard and practical measures to mitigate them.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Falls from Height
- Struck-by Incidents
- Electrocution
- Caught-in or Caught-between Hazards
- Hazardous Materials Exposure
- Machinery and Equipment Accidents
- Trench and Excavation Collapses
- Repetitive Motion Injuries
- Noise and Vibration Hazards
- Slips, Trips, and Falls at Ground Level
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
The construction industry is one of the most hazardous sectors worldwide. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), construction workers accounted for approximately 20% of all worker fatalities in the U.S. despite representing only about 6% of the workforce. This stark statistic highlights the need for vigilance and robust safety protocols.

Understanding the most common hazards on construction sites enables workers, supervisors, and companies to implement targeted safety measures. This post will detail these hazards with examples and advice on prevention.
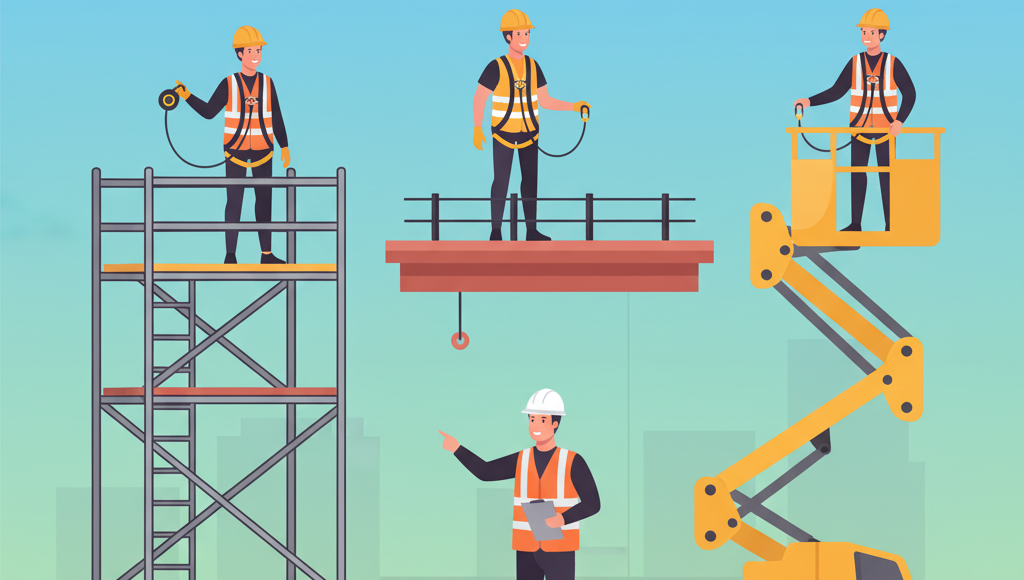
2. Falls from Height
Overview
Falls from height are the leading cause of death in construction. Workers often operate on scaffolding, ladders, roofs, and elevated platforms, increasing the risk.
Causes
- Lack of guardrails or fall protection
- Improper ladder use or faulty scaffolding
- Poor weather conditions making surfaces slippery
- Unsecured edges or openings
Prevention
- Use personal fall arrest systems (PFAS) such as harnesses and lanyards
- Ensure scaffolding and ladders meet safety standards and are inspected regularly
- Install guardrails and toe boards around edges
- Provide fall protection training for all workers
3. Struck-by Incidents
Overview
Struck-by accidents involve workers being hit by falling, flying, swinging, or rolling objects. These incidents often lead to severe injuries.
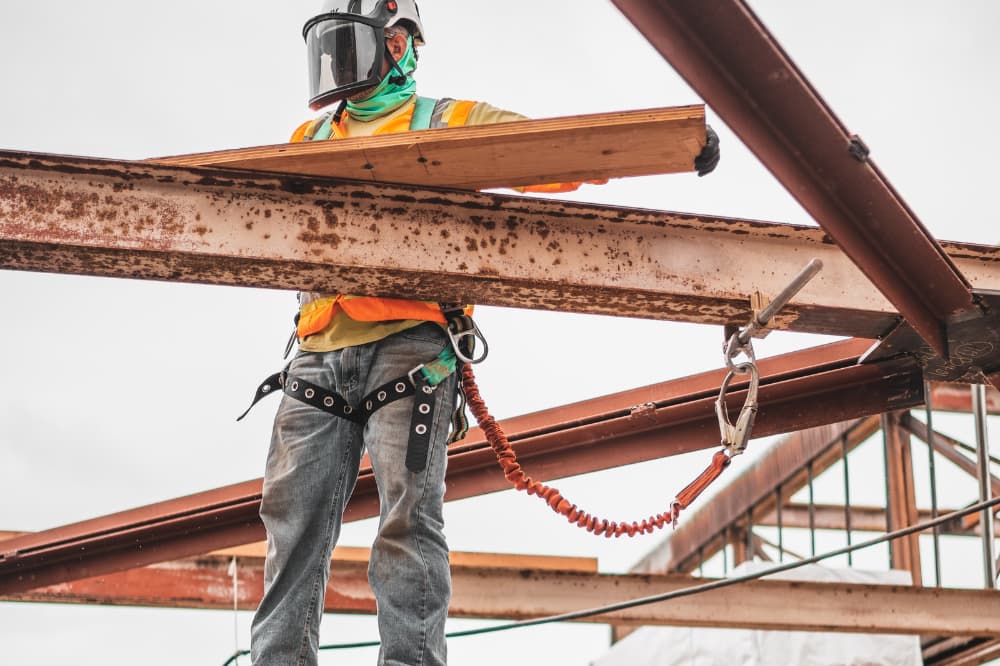

Causes
- Tools or materials dropping from height
- Vehicles and heavy machinery operating near workers
- Swinging cranes or loads
- Debris from demolition or construction activities
Prevention
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), especially hard hats
- Use tool lanyards and secure materials properly
- Maintain clear communication and use spotters around moving equipment
- Establish exclusion zones around high-risk areas
4. Electrocution
Overview
Electrocution is a major hazard due to the use of electrical tools, temporary wiring, and proximity to power lines.
Causes
- Contact with overhead power lines
- Faulty or damaged electrical tools and cords
- Improper grounding or lack of GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter)
- Wet working environments increasing conductivity
Prevention
- Maintain safe distances from power lines and de-energize circuits when possible
- Conduct regular inspections of electrical equipment
- Use GFCI protection on all temporary wiring
- Train workers on electrical safety and lockout/tagout procedures
5. Caught-in or Caught-between Hazards
Overview
These hazards occur when workers are caught inside or compressed by equipment or materials.
Causes
- Trenching or excavation cave-ins
- Rollovers or runovers by heavy machinery
- Being caught between moving parts or between equipment and objects
- Collapsing structures or materials
Prevention
- Use protective systems such as trench boxes and shoring in excavations
- Implement machinery safety protocols including roll-over protective structures (ROPS)
- Train workers on hazard awareness and safe machine operation
- Maintain good housekeeping and secure materials properly
6. Hazardous Materials Exposure
Overview
Construction workers may be exposed to harmful substances such as asbestos, silica dust, solvents, and lead.
Causes
- Demolition or renovation disturbing hazardous materials
- Inhalation of dust or fumes
- Skin contact with chemicals
- Improper storage or handling of hazardous substances
Prevention
- Conduct hazard assessments and air monitoring
- Use appropriate respiratory protection and PPE
- Follow safety data sheets (SDS) and safe handling procedures
- Provide training on hazard communication and emergency response
7. Machinery and Equipment Accidents
Overview
Heavy machinery like cranes, bulldozers, forklifts, and power tools pose significant risks if not operated safely.
Causes
- Lack of training or operator error
- Mechanical failure or poor maintenance
- Inadequate guarding on moving parts
- Improper use of equipment beyond its capacity
Prevention
- Train operators and enforce certification requirements
- Conduct daily inspections and maintain equipment regularly
- Install and maintain guards on machinery
- Follow manufacturer guidelines and site-specific safety protocols
8. Trench and Excavation Collapses
Overview
Excavation work is necessary but risky, with the potential for cave-ins leading to burial or crushing.
Causes
- Unstable soil or water accumulation
- Lack of proper shoring, shielding, or sloping
- Heavy loads or vibrations near trench edges
- Inadequate inspection and hazard recognition
Prevention
- Use protective systems compliant with OSHA standards
- Regularly inspect trenches, especially after rain or other changes
- Restrict heavy equipment near trench edges
- Train workers on excavation safety and emergency procedures
9. Repetitive Motion Injuries
Overview
Tasks involving repeated motions can cause musculoskeletal disorders such as carpal tunnel syndrome or tendonitis.
Causes
- Continuous use of hand tools or power tools without breaks
- Awkward postures or forceful exertions
- Lack of ergonomic equipment or workstation design
- Ignoring early symptoms of strain
Prevention
- Rotate tasks among workers to reduce repetitive strain
- Use ergonomically designed tools and equipment
- Encourage breaks and stretching exercises
- Provide training on proper techniques and early symptom reporting
10. Noise and Vibration Hazards
Overview
High noise levels and vibration exposure can cause hearing loss and other health issues.
Causes
- Operation of heavy machinery and power tools
- Prolonged exposure without hearing protection
- Use of vibrating tools like jackhammers and grinders
Prevention
- Implement a hearing conservation program including regular hearing tests
- Use hearing protection devices such as earplugs or earmuffs
- Limit exposure time and maintain equipment to reduce noise and vibration levels
- Educate workers about the risks and proper use of protective gear
11. Slips, Trips, and Falls at Ground Level
Overview
While falls from height are critical, many injuries occur from slips or trips on the same level.
Causes
- Uneven ground or debris on walkways
- Wet or oily surfaces
- Poor lighting or cluttered work areas
- Inadequate footwear
Prevention
- Maintain clean and organized work areas
- Use slip-resistant footwear and signage for hazardous areas
- Ensure adequate lighting in all work zones
- Promptly address spills and hazards
12. Conclusion
Safety on construction sites requires a proactive approach to identify and control hazards. The ten hazards discussed here represent the most common and dangerous risks workers face daily. Employers and workers must collaborate through training, use of proper equipment, adherence to safety standards, and ongoing vigilance to minimize accidents and injuries.
By understanding these hazards and implementing effective control measures, the construction industry can move closer to its goal of zero accidents and a safer working environment for all.
References
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
- Center for Construction Research and Training (CPWR)
This post aims to provide construction professionals and safety managers with a detailed overview of critical safety hazards and practical ways to address them. Regular updates and continuous education are essential as technologies and regulations evolve. Stay safe and prioritize safety every day on site!