The construction industry has always been a cornerstone of human development, shaping the infrastructure and landscapes that define our societies. As we move through 2025, the sector is experiencing a technological revolution unlike any before. From advanced robotics to AI-driven project management, construction technology is transforming how buildings are designed, constructed, and maintained. This blog post explores the key technological trends and innovations that are reshaping construction in 2025, the benefits they bring, and the challenges that come with adopting these new tools.
Introduction
Construction has traditionally been a labor-intensive, time-consuming, and often hazardous industry. However, rapid advancements in technology are driving a paradigm shift. The integration of digital tools and automation is improving efficiency, safety, and sustainability, while reducing costs and timelines. In 2025, the industry is not just adopting new technologies but is evolving into a data-driven, highly connected ecosystem.

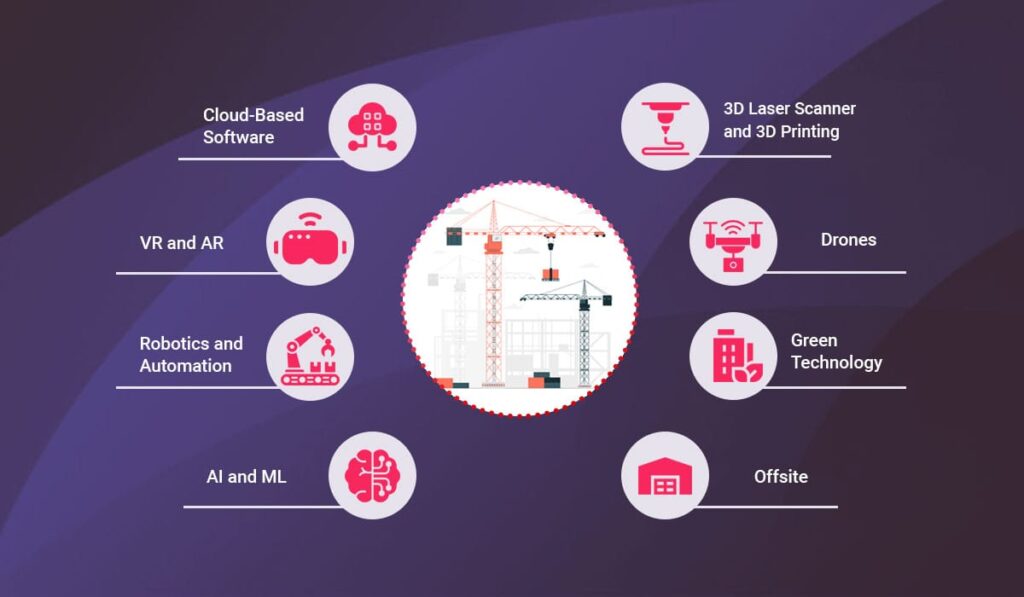
This comprehensive analysis covers the most influential construction technologies of 2025, including:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Robotics and Automation
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) 2.0
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
- Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Sensors
- Sustainable Construction Technologies
- 3D Printing and Modular Construction
- Drones and Aerial Data Collection
- Cloud Computing and Project Management Software
- Blockchain for Construction Contracts and Supply Chain
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a game changer in construction technology. In 2025, AI is no longer confined to theoretical applications but is deeply embedded in everyday construction processes.

AI-Powered Project Planning
AI algorithms analyze historical project data, weather patterns, supply chain information, and workforce availability to create optimized project plans. This predictive capability helps in avoiding delays and budget overruns by anticipating risks and suggesting mitigation strategies early on.
Quality Control and Safety Monitoring
Machine learning models are trained to identify patterns that indicate potential safety hazards or quality issues. For example, AI-powered cameras on-site can detect if workers are not wearing protective equipment or if materials are stored improperly, sending instant alerts to supervisors.
Predictive Maintenance
AI also plays a critical role in predictive maintenance of construction equipment. Sensors collect data on machinery performance, which AI analyzes to predict failures before they happen, reducing downtime and repair costs.
2. Robotics and Automation
Robots and automated machinery are increasingly common on construction sites, performing tasks that were once labor-intensive, repetitive, or dangerous.
Autonomous Machinery
Excavators, bulldozers, and cranes equipped with autonomous navigation systems are capable of working with minimal human intervention. This reduces human error and increases operational efficiency.
Robotic Bricklaying and Concrete Printing
Robotic bricklayers and 3D concrete printers can build walls faster and with higher precision than manual labor. These robots are programmable to create complex structures and can work continuously, accelerating project timelines.
Exoskeletons for Workers
Wearable robotic exoskeletons assist construction workers by reducing strain and fatigue, enabling them to lift heavy loads safely and work longer hours without injury.
3. Building Information Modeling (BIM) 2.0
Building Information Modeling has evolved into BIM 2.0, an intelligent, integrated platform that connects every stakeholder throughout the construction lifecycle.
Real-Time Collaboration
BIM 2.0 enables real-time collaboration among architects, engineers, contractors, and clients by integrating design, scheduling, cost estimation, and logistics into a single digital model accessible from anywhere.
Enhanced Visualization and Simulation
With BIM 2.0, simulations of structural performance, energy efficiency, and construction sequencing are more detailed and accurate, allowing teams to identify and address potential issues before breaking ground.
Digital Twins
BIM models now serve as digital twins — virtual replicas of physical buildings that update in real time throughout construction and operation, facilitating maintenance and management post-completion.
4. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies are revolutionizing design visualization, training, and on-site assistance.
Design and Client Engagement
VR allows clients and stakeholders to immerse themselves in virtual walkthroughs of proposed buildings, making it easier to understand design intent and provide feedback.
On-Site AR Assistance
AR headsets worn by construction workers overlay digital information — such as blueprints, safety alerts, and installation instructions — directly onto the physical environment, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
Training and Safety Drills
VR simulations create safe, controlled environments for worker training, including hazard recognition and emergency response drills, significantly improving safety outcomes.
5. Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Sensors
IoT devices and sensors embedded throughout construction sites collect real-time data on environmental conditions, equipment usage, and worker health.
Environmental Monitoring
Sensors monitor parameters like temperature, humidity, dust levels, and noise pollution to ensure compliance with safety regulations and minimize environmental impact.
Equipment and Asset Tracking
IoT enables precise tracking of equipment location, usage, and maintenance needs, optimizing asset management and reducing theft or loss.
Worker Health and Safety
Wearable IoT devices monitor worker vital signs and fatigue levels, alerting supervisors to potential health risks and preventing accidents.
6. Sustainable Construction Technologies
Sustainability is a top priority in 2025 construction, driven by regulatory pressures and client demand for eco-friendly buildings.
Green Building Materials
Innovations include bio-based materials, recycled content composites, and low-carbon concrete alternatives that reduce the environmental footprint of construction.
Energy-Efficient Systems
Smart HVAC, lighting, and water management systems integrated at design and construction stages optimize building performance and reduce operational costs.
Waste Reduction Technologies
Advanced waste sorting and recycling technologies minimize landfill contributions, while digital tools optimize material ordering to prevent excess.
7. 3D Printing and Modular Construction
The convergence of 3D printing and modular construction is transforming how buildings are assembled.
Large-Scale 3D Printing
Construction-scale 3D printers can fabricate walls, facades, and structural components on-site using concrete and composite materials, reducing labor and material waste.
Modular Prefabrication
Prefabricated modules constructed in controlled factory settings ensure higher quality standards and faster assembly on-site, dramatically shortening project durations.
Customization and Complexity
3D printing and modular techniques enable the creation of complex architectural designs and customized components that were previously cost-prohibitive.
8. Drones and Aerial Data Collection
Drones continue to expand their role in construction site monitoring and data collection.
Site Surveying and Mapping
High-resolution aerial photogrammetry and LiDAR scans generate precise topographic maps and 3D models, aiding in planning and progress tracking.
Safety Inspections
Drones access hard-to-reach or hazardous areas to conduct safety inspections without putting workers at risk.
Inventory Management
Aerial views help monitor inventory stockpiles and delivery status, preventing material shortages or overstocking.
9. Cloud Computing and Project Management Software
Cloud-based platforms are central to construction project coordination, offering enhanced communication, transparency, and data security.
Integrated Project Delivery (IPD)
Cloud software facilitates IPD by connecting all parties — including subcontractors and suppliers — through shared dashboards, document repositories, and communication channels.
Real-Time Reporting and Analytics
Project managers access real-time data on progress, costs, and resource allocation, enabling dynamic decision-making and rapid problem resolution.
Mobile Access
Mobile apps allow workers and supervisors to access schedules, blueprints, and safety protocols directly from the field, improving responsiveness.
10. Blockchain for Construction Contracts and Supply Chain
Blockchain technology addresses issues of transparency, trust, and efficiency in construction contracts and supply chains.
Smart Contracts
Blockchain-enabled smart contracts automate payments and compliance verification, reducing disputes and administrative overhead.
Supply Chain Traceability
Immutable blockchain records verify the provenance and quality of materials, enhancing accountability and reducing fraud.
Collaborative Ecosystems
Blockchain platforms create decentralized networks where multiple stakeholders can securely share information and collaborate with confidence.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of construction technology in 2025 are substantial, there are challenges to widespread adoption:
- High Initial Costs: Advanced equipment and software require significant upfront investment.
- Skill Gaps: The workforce needs ongoing training to effectively use new technologies.
- Data Security: Increased digitalization raises concerns about cyber threats and data privacy.
- Regulatory Compliance: Evolving laws and standards must keep pace with technological innovation.
- Integration Complexity: Combining multiple new technologies into existing workflows can be difficult.
Conclusion
The construction industry in 2025 is at the forefront of a technological transformation that promises safer, faster, and more sustainable building practices. AI, robotics, BIM 2.0, AR/VR, IoT, and other innovations are not only enhancing productivity but also creating new opportunities for creativity and efficiency. While challenges remain, companies that embrace and adapt to these technologies will lead the future of construction, delivering projects that meet the demands of a rapidly changing world.
As we look ahead, continuous innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to sustainability will be essential in harnessing the full potential of construction technology. The buildings and infrastructure of tomorrow will be smarter, greener, and more resilient — all thanks to the technological advances shaping construction today.
Further Reading and Resources
- McKinsey & Company: “The Next Normal in Construction”
- World Economic Forum: “Shaping the Future of Construction”
- Construction Industry Institute: Research on Robotics and Automation
- Autodesk BIM 360: Latest BIM Tools and Innovations
- IEEE Construction Technology Journal: AI and IoT Applications
Thank you for reading! Stay tuned

